500 a Day
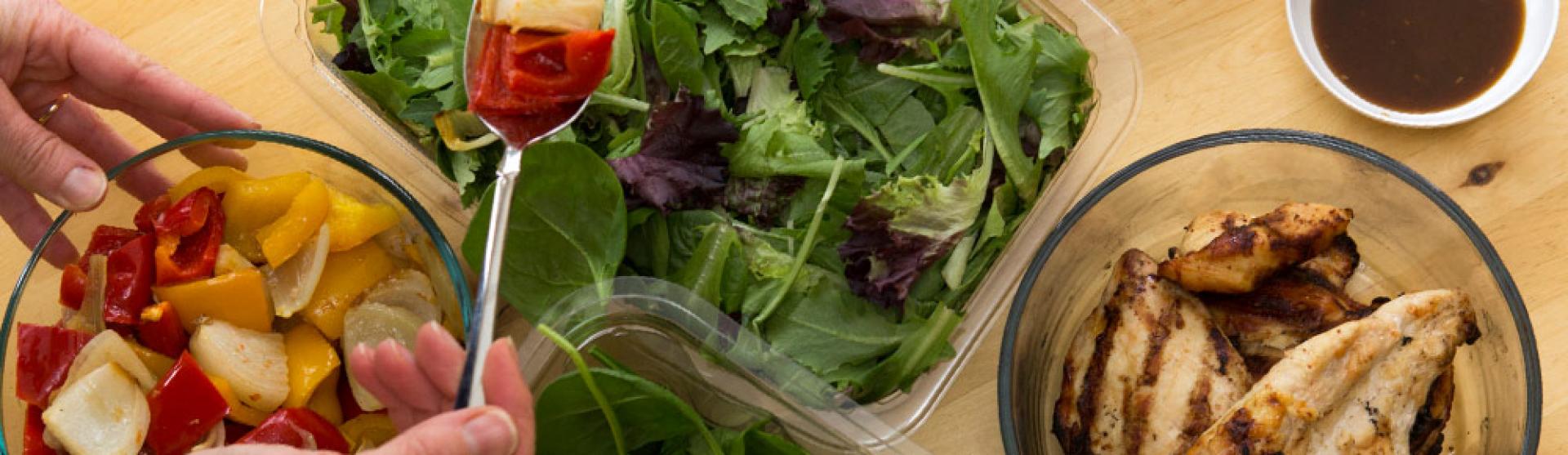
It may sound like a lot, but 500 calories is about the amount you get in a small fast-food shake. However, you can enjoy more to eat—and get the nutrition you need—by skipping high-calorie, low-nutrient foods like this and choosing basic whole foods instead. Like fruits and vegetables, lean meats, poultry, seafood low in mercury, skim milk or low-fat yogurt, and whole grains.
Nutritious Suggestions
Moms who breastfeed exclusively need a nutritious diet to keep up with their health. To hit your health goals for you and your baby, try a well-balanced daily diet including:
- 2 cups fruit
- 3 cups vegetables
- 8 oz. grains
- 6½ oz. meat or beans
- 3 cups skim milk or foods made with milk, like cheese or yogurt
- Your need for fluids increases while you’re breastfeeding. Drink enough water and other fluids to quench your thirst.
- Speak to your doctor about continuing prenatal vitamins and a DHA supplement to make sure you're getting the nutrients you need.
*These amounts are for an average breastfeeding woman. You may need more or less than the average. Check with your health care provider for the amounts appropriate for you.
The Nutrients You Need Most
There are some specific nutrients that your body needs while lactating, in order to make breastmilk and help support your personal health. It's even more important to make sure you're getting it all if you’re a vegetarian or restricting one or more food groups.
Calcium
Helps build and maintain strong bones. Calcium is absorbed better when consumed with Vitamin D.
Good sources: milk, cheese, yogurt, canned salmon, dark green leafy vegetables, beans and lentils, calcium-fortified cereals and 100% fruit juice that is calcium-fortified.
Iron
Carries oxygen to your blood, maintains energy level and can help protect from infections. Iron from vegetable sources can be absorbed better when consumed along with foods rich in Vitamin C.
Good sources: all meats, especially lean beef and poultry; Iron-fortified cereal, spinach and beans.
Zinc
Important for healing and cell reproduction.
Good sources: lean meat, poultry, beans, nuts, zinc-fortified cereal, low-fat or fat-free dairy, whole-grain bread.
Protein
Keeps tissues and cells in good repair. Protein needs increase for breastfeeding moms by about 25 grams—the amount in about three ounces of lean meat, poultry or fish.
Good sources: lean meat, skinless poultry, fish, low-fat or fat-free milk and dairy products, eggs, cooked dry beans, peas and nuts.
Vitamin D
Helps the body use calcium and phosphorus, supports the immune system.
Good sources: low-fat or fat-free milk fortified with vitamin D, fatty fish such as salmon and tuna, vitamin D-fortified cereal, exposure to direct sunlight.
Vitamin B12
Supports your body’s metabolism and your immune system. Works with folic acid to form hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Good sources: beef liver, lean meat, skinless poultry, fish, clams, vitamin B12-fortified cereal, low-fat or fat-free milk, eggs
DHA
Helps support brain and eye development. It is found naturally in breastmilk but the amount depends on your diet.
Good sources: Fish such as tuna and salmon, fortified products, DHA supplement (talk to your doctor about continuing to take yours)
Choline
Helps support brain development
Good sources: Eggs, fish, wheat germ, choline supplement (talk to your doctor about continuing yours)